Alibaba's QwQ 32B model challenges OpenAI's o1 mini, o1 preview, claude 3.5 sonnet and gpt4o and its open source
Alibaba's QwQ-32B challenges top models, Andrew Ng releases universal LLM framework, NVIDIA speeds inference, Deepseek cuts costs, and LLMs master neuroscience predictions.
In today’s Edition (28th Nov-2024):
Alibaba QwQ 32B model challenges OpenAI's o1 mini, o1 preview, claude 3.5 sonnet and gpt4o and its open source
Andrew Ng introduces aisuite framework, that makes it easy to interact with the most popular LLMs and compare the results, by changing one line.
NVIDIA introduces Star Attention achieving 11x faster LLM inference with 95% accuracy
Deepseek cuts LLM costs by 93% through smarter memory management while being competitive with OpenAI's o1. It’s CEO’s interview.
🧠 New nature published research shows, LLMs predict neuroscience experiment outcomes better than human experts, achieves 81% accuracy
Alibaba’s QwQ 32B model challenges OpenAI's o1 mini, o1 preview, claude 3.5 sonnet and gpt4o and its open source
The Brief
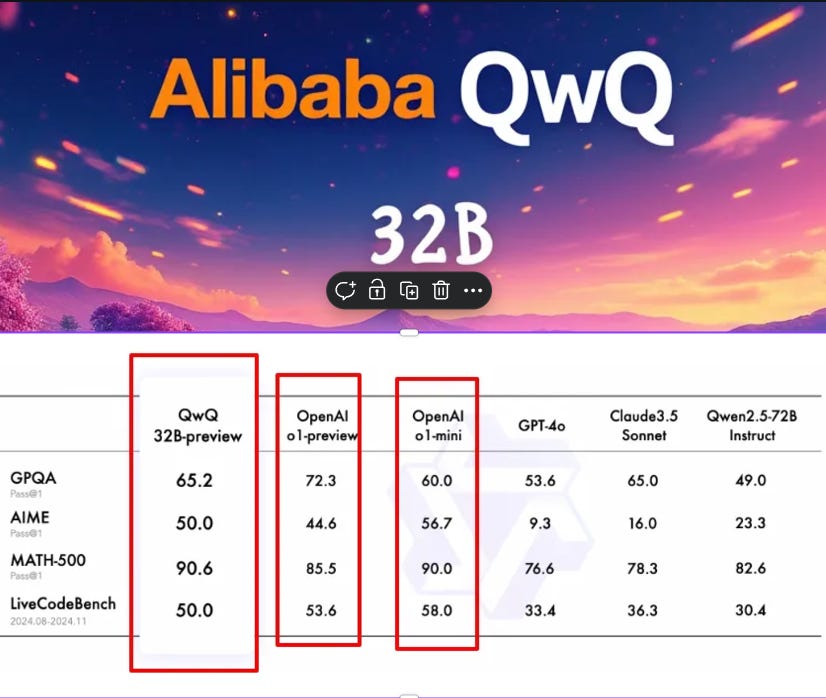
Qwen Team launches QwQ-32B-Preview, an experimental LLM focused on deep reasoning, achieving 90.6% on MATH-500 benchmark and competing with OpenAI's models through systematic self-questioning approach.
The Details
→ QwQ implements unique introspective reasoning style, questioning assumptions and exploring multiple solution paths before providing answers. The model's analytical process mimics skilled human problem-solvers.
→ Unlike traditional LLMs that directly output answers, QwQ engages in internal dialogue. It breaks down problems into smaller parts, considers multiple possibilities, and openly acknowledges its thought process - including dead ends and revised approaches.
→ The model displays exceptional proficiency in mathematical reasoning and code generation. The demo showcases its ability to solve intricate mathematical equations through systematic exploration of different approaches until finding the correct solution.
→ Benchmark performances showcase technical prowess: 65.2% on GPQA, 50.0% on AIME, 90.6% on MATH-500, and 50.0% on LiveCodeBench.
→ Core innovations include process reward models for structured reasoning, LLM critique mechanisms for self-analysis, multi-step reasoning for complex problem decomposition, and system feedback integration.
→ Key limitations identified: language mixing issues, recursive reasoning loops, safety concerns, and uneven performance across different domains.
The model is available in HuggingFace
Some Limitataions
Few reported the model is notably "chatty" in its reasoning, using up to 3,846 tokens for simple questions at temperature=0 (compared to 1,472 for O1). The model requires a specific system prompt mentioning "You are Qwen developed by Alibaba" for optimal performance.
The Impact
This advancement signals a shift toward more thoughtful, systematic AI reasoning approaches and achieving this with Open-Source model can open up many possibilities.
Andrew Ng introduces aisuite framework, that makes it easy to interact with the most popular LLMs and compare the results, by changing one line
The Brief
Andrew Ng introduces aisuite, an open-source Python framework enabling seamless testing of multiple LLMs through a standardized interface by changing just one string, significantly simplifying LLM integration and experimentation.
The Details
→ Aisuite implements a unified interface similar to OpenAI's API, allowing developers to switch between LLMs using a simple string format: :. The framework supports nine major providers including OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure, Google, AWS, Groq, Mistral, HuggingFace, and Ollama.
→ The framework focuses on chat completions through HTTP endpoints or SDKs. Installation options include base package, provider-specific installations, or comprehensive all-provider setup. The modular architecture follows strict naming conventions with _provider.py format for modules and Provider for classes.
The Impact
This streamlines LLM testing and integration, enabling rapid model comparisons and flexible workflows without managing multiple APIs.
NVIDIA introduces Star Attention achieving 11x faster LLM inference with 95% accuracy
The Brief
NVIDIA introduces Star Attention, a novel attention mechanism for efficient LLM inference over long sequences, achieving up to 11x speedup while maintaining 95-100% accuracy through a two-phase block-sparse approximation approach.
The Details
→ Star Attention utilizes a unique two-phase architecture. The first phase processes context through blockwise-local attention across multiple hosts in parallel. Each block is prefixed with an "anchor block" - the first segment of the sequence - which helps manage attention patterns and approximates global attention behavior.
→ The second phase employs sequence-global attention where query and response tokens attend to all cached tokens. This distributed approach minimizes communication overhead by requiring only a single vector and scalar per token from each context host.
→ Performance testing on Llama-3.1-8B and Llama-3.1-70B models shows exceptional results. Setting block size to one-quarter of sequence length provides optimal balance between speed and accuracy. The method excels particularly in single-lookup tasks and aggregation tasks, though shows some degradation in multi-hop scenarios requiring cross-block communication.
The Impact
Star Attention represents a significant advancement in making LLM inference more efficient and scalable. Its ability to process sequences up to 1M tokens while maintaining high accuracy opens possibilities for applications like repository-level code analysis and large corpus retrieval.
Deepseek cuts LLM costs by 93% through smarter memory management while being competitive with OpenAI's o1.
The Brief
Chinese AI startup Deepseek unleashes unprecedented price disruption in LLM market by launching DeepSeek V2 with groundbreaking MLA architecture, reducing inference costs to 1 RMB per million tokens - 1/70th of GPT-4 Turbo cost. Learn more details from it’s CEO’s interview.
The Details
→ Deepseek, backed by $8 billion hedge fund High-Flyer, possesses estimated 50,000 Hopper GPUs. Their MLA architecture slashes memory usage to 5-13% of standard MHA, while DeepseekMoESparse structure minimizes computational costs.
→ Unlike other Chinese AI firms focusing on applications, Deepseek commits to open-source research and foundational innovation. CEO Liang Wenfeng maintains no external fundraising plans, focusing solely on AGI development.
→ Their team comprises primarily young local graduates rather than overseas returnees. They implement a bottom-up innovation structure where researchers get unrestricted access to compute resources and cross-team collaboration.
The Impact
This marks China's first significant contribution to global LLM architectural innovation, challenging the notion that Chinese companies excel only at applications. The price war triggered by Deepseek's release forced major tech giants like ByteDance, Alibaba, and Tencent to slash their API prices, potentially democratizing AI access.
🧠 New nature published research shows, LLMs predict neuroscience experiment outcomes better than human experts, achieves 81% accuracy
The Brief
New research paper on BrainGPT demonstrates that LLMs outperform human experts in predicting neuroscience experimental outcomes, achieving 81.4% accuracy compared to experts' 63.4%, marking a significant advancement in AI's ability to synthesize scientific literature for discovery.
The Details
→ Researchers created BrainBench, a forward-looking benchmark that tests LLMs' ability to predict neuroscience results by choosing between original and altered research abstracts. The benchmark spans five domains: behavioral/cognitive, cellular/molecular, systems/circuits, neurobiology of disease, and development/plasticity/repair.
→ All tested LLMs, including smaller 7B parameter models, surpassed human performance. The performance stems from LLMs' ability to integrate information across entire abstracts, including methods and background sections. When restricted to local context, performance dropped significantly.
→ Using LoRA fine-tuning on 1.3 billion tokens of neuroscience literature, researchers created BrainGPT by adapting Mistral-7B, improving accuracy by 3%. Both LLMs and human experts showed well-calibrated confidence ratings, with higher confidence correlating with better accuracy.
The Impact
This breakthrough suggests LLMs could serve as powerful tools for scientific discovery by helping researchers predict experimental outcomes and optimize study designs. The approach could extend beyond neuroscience to other knowledge-intensive fields, potentially accelerating scientific progress.
Byte-Size Brief
Local integration of LLaMa-Mesh in Blender just released. This is a Blender addon for generating meshes with AI
A comprehensive evaluation of 5 SOTA LLMs on Kazakhstan's olympiad programming problems showed impressive performance of open-source model QwQ from Alibaba Qwen and R1-Lite from Deepseek_ai. OpenAI’s o1-mini led with 266 points, followed by r1-lite (209), qwq (195), Claude Sonnet (52), and GPT-4 (32). Problems were chosen for being Russian-only and lacking public solutions, enabling true capability assessment.
AWS's Open-Source Framework Transforms Multi-Agent AI Development. AWS launched an open-source multiagent AI framework enabling real-time orchestration of specialized AI agents. The system supports Python/TypeScript, handles streaming responses, maintains conversation context, and includes pre-built agents for domains like travel, weather, math, and health, with built-in classifiers for dynamic query routing between agents.
Novel new Paper "Multi-Head Mixture-of-Experts". Instead of one big AI brain, MH-MoE uses multiple smaller experts working together - like a team of specialists. MH-MoE implements multi-head attention principles in mixture-of-experts architecture, enabling parallel processing through specialized neural pathways. The model maintains computational efficiency while achieving superior performance on language tasks through optimized expert routing and information integration across representation spaces.