Beyond Browsing: API-Based Web Agents
AI Web agents ditch clicking buttons, talk directly to servers through APIs to get tasks done faster.
AI Web agents ditch clicking buttons, talk directly to servers through APIs to get tasks done faster.
Original Problem 🎯:
Web agents primarily rely on browser interfaces designed for humans, making them inefficient for machine-to-machine interactions. Current web browsing agents achieve limited success rates due to complex GUI navigation and accessibility tree limitations.
Solution in this Paper 🔧:
• Introduces two agent types: API-Based Agent and Hybrid Agent
• API-Based Agent directly communicates with web services through documented APIs
• Hybrid Agent combines API calls with web browsing capabilities
• Implements two-stage documentation retrieval for large API sets
• Uses GPT-4 to generate documentation for undocumented APIs
• Leverages OpenHands framework for agent evaluation and development
Key Insights from this Paper 💡:
• APIs offer more efficient task completion compared to browser-based interactions
• API availability and quality significantly impact agent performance
• Hybrid approach provides flexibility to handle both API-supported and unsupported tasks
• Well-documented APIs lead to higher success rates in task completion
• Manual API integration remains a current limitation
Results 📊:
• Hybrid Agent achieves 35.8% success rate on WebArena benchmark
• API-Based Agent outperforms browsing agents by 15% on average
• Hybrid Agent shows 20% absolute improvement over web browsing alone
• Best performance on GitLab (44.4%) and Map (45.9%) tasks
• Reduced number of steps: API agent (7.8) vs Browsing agent (8.4)
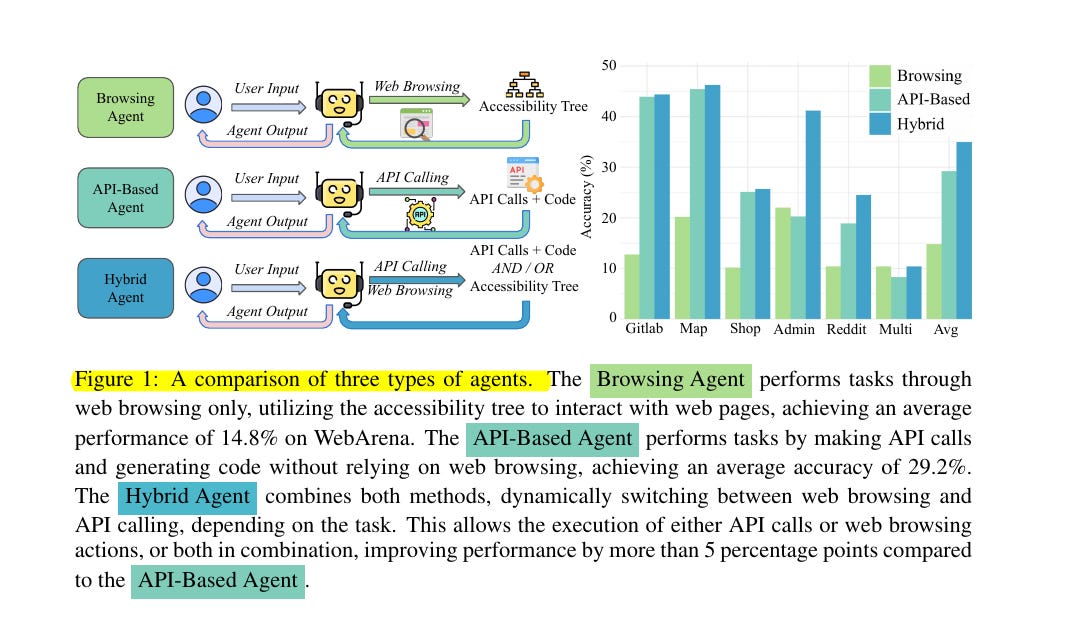
🚀 How do the three types of agents (Browsing, API-Based, and Hybrid) compare in performance?
Browsing Agent: 14.8% average success rate using only web browsing actions
API-Based Agent: 29.2% average success rate using only API calls
Hybrid Agent: 35.8% average success rate by combining both methods The Hybrid Agent outperforms both other approaches by dynamically switching between API calls and web browsing based on task requirements.