Google's new Gemini 2.0 breaks new ground in AI
OpenAI voice services scale globally, Gemini 2.0 powers Code Assist, HuggingFace's synthetic data generation, plus WebRTC API implementation guide.
⚡In today’s Edition (18-Dec-2024):
🏆 Google Rolling Out Gemini 2.0 Advanced Model to Paid Subscribers
🤙 OpenAI launches ChatGPT voice service reaching users through 1-800 number and WhatsApp globally
🎯 GitHub launches a free version of its Copilot
🤗 Synthetic Data Generator dropped in Huggingface, a no-code tool that enables dataset generation through natural language prompts
🛠️ Google upgrades its programming agent Code Assist with Gemini 2.0, adds source integrations
👨🔧 OpenAI API changed, No more “system” prompts, say hello to the "developer" prompt.
🦙 Llama-3 8B outperformS Llama-3 70B on hard math by scaling test-time compute, by HuggingFace researchers
🧑🎓 Deep Dive Tutorial
🌐 Implement OpenAI's Realtime API with WebRTC with full code.
🏆 Google Rolling Out Gemini 2.0 Advanced Model to Paid Subscribers
🎯 The Brief
Google rolls out a new 2.0 Experimental Advanced model, Gemini-Exp-1206, exclusively for Gemini Advanced subscribers via web interface. The model ranks #1 on LMSYS LLM Leaderboard with a score of 1374, surpassing GPT-4. Also offered a 1-month free access.
⚙️ The Details
→ The model showcases enhanced capabilities in complex coding tasks, mathematics, reasoning, and instruction following. A standout feature is its ability to provide detailed multi-step DIY instructions, addressing previous model limitations.
→ Access is restricted to web-based interface only, with model selection available through the switcher option. Current limitations include no real-time information access and incompatibility with certain Gemini features.
→ This release follows the recent Gemini 2.0 Flash deployment on Android, demonstrating Google's strategic expansion in premium AI offerings. The model's early preview status means occasional performance inconsistencies may occur.
→ Additionally, this model will not have access to real-time information and won't be compatible with some Gemini features in its experimental state. You can access our 2.0 Experimental Advanced model in Gemini Advanced on desktop and mobile web. You also get a 2 TB of storage with Gemini Advanced subscription.
→ To date, Gemini Advanced has given subscribers access to 1.0 Ultra and 1.5 Pro models. As such, it’s possible that Gemini-Exp-1206 is 2.0 Pro or higher. Google said to expect more Gemini 2.0 model sizes in January when 2.0 Flash hits general availability for developers. Gemini Advanced requires the $19.99 per month Google One AI Premium subscription.
🤙 OpenAI launches ChatGPT voice service reaching users through 1-800 number and WhatsApp globally
🎯 The Brief
OpenAI launches ChatGPT voice service through phone calls and WhatsApp, making AI accessible via traditional communication channels. The service works through 1-800-ChatGPT (1-800-242-8478) in the US and globally through WhatsApp integration.
⚙️ The Details
→ The phone service operates on the GPT-4o Mini model, supporting both voice calls and text messaging. Users get 15 minutes of free calling monthly with US phone numbers, with extended access available through the app.
→ The system has compatibility across device generations - from modern smartphones to legacy rotary phones, showcasing robust telephony integration. The service handles diverse queries ranging from basic information to technical explanations.
→ WhatsApp integration enables global accessibility, allowing users to interact with ChatGPT through text messaging. The system processes requests continuously and sends responses in segments until completion.
→ The technology supports multilingual capabilities, real-time conversation, and domain expertise across various topics from recipe modifications to technical concepts.
🎯 GitHub launches a free version of its Copilot
🎯 The Brief
GitHub just introduced today a free tier of its Copilot AI coding assistant, bundling it with VS Code editor. The platform now serves 150 million developers, up 50% from previous year. Free tier offers 2,000 monthly code completions and 50 chat messages, with access to Claude 3.5 Sonnet and GPT-4o models.
⚙️ The Details
→ The free version represents a strategic shift from GitHub's previous $10/month pricing model. This move expands beyond their earlier free access limited to students and open-source maintainers
→ Technical constraints include counting each Copilot suggestion against the monthly limit, regardless of user acceptance. Free tier users get restricted foundation model access compared to paid users who receive additional models like Gemini 1.5 Pro, o1-preview, and -mini
→ Platform integration extends across multiple development environments including VS Code, Visual Studio, JetBrains, and GitHub.com. This positions GitHub against competitors like Tabnine, Qodo, and AWS CodeWhisperer who already offer free tiers
→ CEO Thomas Dohmke emphasizes this aligns with GitHub's vision of enabling one billion developers globally. The strategy particularly targets emerging markets where monthly fees present significant barriers to adoption
→ The decision stems from analyzing years of Copilot usage data to determine optimal thresholds between casual and professional developers, ensuring accessibility while maintaining service quality
🤗 Synthetic Data Generator dropped in Huggingface, a no-code tool that enables dataset generation through natural language prompts
🎯 The Brief
Imagine creating custom datasets and training AI models WITHOUT writing a single line of code. That’s what Synthetic Data Generator is, a no-code application for creating custom datasets using LLMs, enabling 50 samples/minute for text classification and 20 samples/minute for chat data generation through the free HuggingFace API.
⚙️ The Details
→ Tool supports text classification and chat datasets through a three-step process: dataset description, configuration refinement, and generation with direct push to Argilla and HuggingFace Hub. Features seamless integration with AutoTrain for codeless model training.
→ System includes advanced customization options through environment variables, allowing users to modify models (like meta-llama/Llama-3.1-70B-Instruct), adjust batch sizes, and switch between API providers. Available as open-source under Apache 2 license, installable via pip.
→ Built on distilabel framework, offering reproducible pipelines and direct integration with Argilla for dataset exploration and evaluation. Supports both cloud deployment on HuggingFace Spaces and local installation.
🛠️ Google upgrades its programming agent Code Assist with Gemini 2.0, adds source integrations
🎯 The Brief
Google upgrades Code Assist (it’s set of tools helps developers increase productivity in IDEs) with Gemini 2.0 integration and adds third-party DevOps platform connections, enhancing enterprise code development capabilities through expanded integrations with GitLab, GitHub, Google Docs, Sentry.io, Atlassian, and Snyk. This positions Code Assist as a comprehensive enterprise-grade coding solution in response to 39% of developers expressing distrust in AI-generated code.
⚙️ The Details
→ Code Assist, previously known as Duet AI, now runs on Gemini 2.0, offering larger context windows for enterprise codebases. The platform enables developers to access contextual information directly within their IDEs, streamlining the coding workflow.
→ The integration ecosystem expands with support from major players including Dynatrace, New Relic, Black Duck, Harness, MongoDB, Neo4j, and others. Natural language commands convert to API calls via OpenAPI standard or YAML, secured through OAuth authentication.
→ Those integrations, for example, will make it simpler to summarize recent comments from a Jira issue, find the last person who merged changes to a file in a Git repository or identify the most recent live site issue.
→ Code Assist remains separate from Jules, Google's experimental coding tool, maintaining its position as the only enterprise-grade coding solution powered by Gemini.
👨🔧 OpenAI API changed, No more system prompts, say hello to the "developer" prompt.
🎯 The Brief
OpenAI introduces "developer" role to replace traditional “system” prompts in their API, representing a restructuring of their prompt hierarchy system. The change reflects a more precise designation of prompt types and their command authority in the API's instruction-following architecture.
⚙️ The Details
→ The new developer role takes priority over user messages in the instruction hierarchy, serving as the primary method for setting model behavior and response patterns. This change maintains the same functionality as the former system prompts but with clearer semantic purpose.
→ Implementation requires specific message structure with role and content fields. The API supports different message roles including user, developer, and assistant, each serving distinct purposes in the conversation flow.
→ Models like gpt-4o feature significant capabilities with a 128k token context window and can generate up to 16,384 output tokens. The API maintains stateless operations but enables multi-turn conversations through message arrays.
→ Developer prompts can define model personality, response style, and behavioral constraints, offering granular control over model outputs while maintaining precedence in the instruction chain of command.
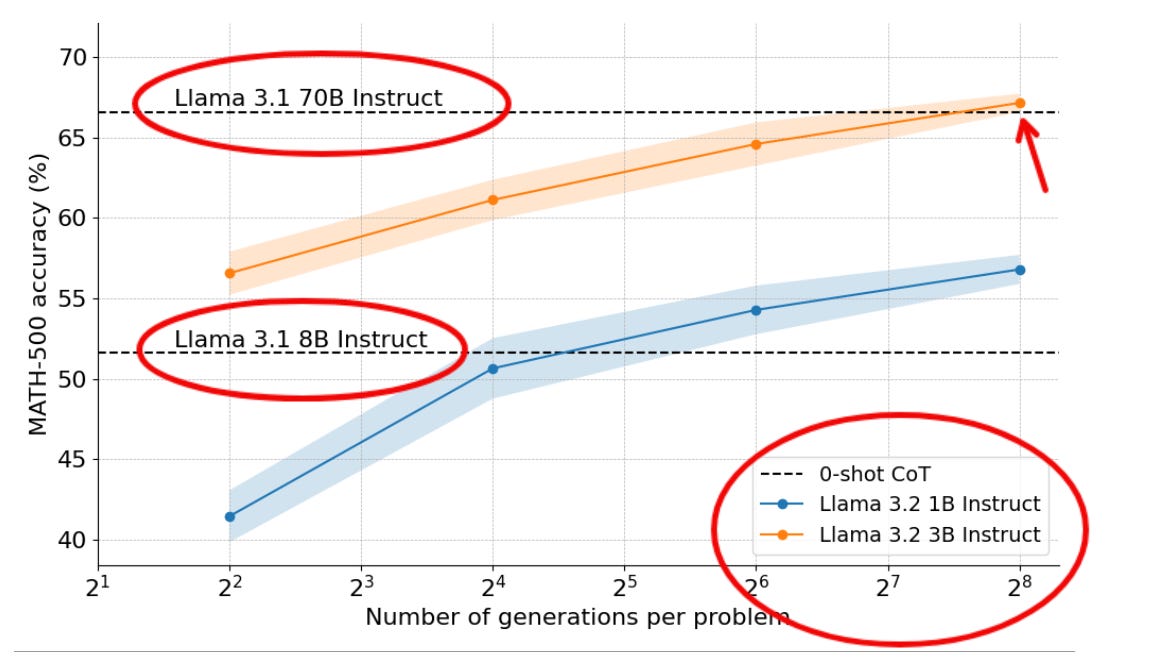
🦙 Llama-3 8B outperformS Llama-3 70B on hard math by scaling test-time compute, by HuggingFace researchers
🎯 The Brief
HuggingFace researchers successfully demonstrated that a 3B parameter Llama model can outperform its 70B counterpart on complex math problems through optimized test-time compute scaling and advanced search strategies, challenging conventional wisdom about model size requirements.
⚙️ The Details
→ The research implemented majority voting (self-consistency decoding) as baseline, using 256 candidates with temperature 0.8 and generating 2048 tokens per problem. The methodology involved testing search strategies across compute budgets from 1 to 256 generations per prompt, with 5 random seeds for variance estimation.
→ A critical improvement came from prompt engineering, by adaptively allocating test-time compute per prompt. The team discovered that switching from a basic prompt to Meta's official MATH benchmark prompt significantly boosted performance beyond the initial 30.6% accuracy. The benchmark required specific formatting with answers .
→ The success stemmed from combining step-wise reward models with tree search algorithms, demonstrating that smaller models can achieve superior performance when given sufficient computational resources for reasoning.
🖌️ Google Labs just released Whisk, a new image generator that lets you input a subject, scene, and style to remix images
🎯 The Brief
Google Labs launched Whisk, a new AI experiment that transforms image generation by using images as prompts instead of text, streamlining creative workflows through a two-stage pipeline combining Gemini and Imagen 3 models.
⚙️ The Details
→ Whisk's architecture employs a unique three-input system: subject image, scene image, and style reference. The system processes these through Gemini for automatic caption generation, which then feeds into Imagen 3 for final image synthesis.
→ The platform focuses on creative exploration rather than precise editing. Users can modify underlying prompts and iterate through multiple design variations quickly. The system captures essential characteristics instead of creating exact replicas, allowing for novel combinations of subjects, scenes, and styles.
→ Technical limitations include selective feature extraction, which may alter physical attributes like height and skin tone in the output. The tool is currently available exclusively in the US through labs.google/whisk.
🧑🎓 Deep Dive Tutorial
🌐 Implement OpenAI's Realtime API with WebRTC with full code.
OpenAI's Realtime API uses WebRTC for direct browser-based voice interactions with AI models. An usecase for example, now you can talk to GPT-4o through your browser's microphone
📚 What you will learn from this blog
Implement secure WebRTC connections in browsers for real-time AI voice chat
Set up peer-to-peer audio streaming using RTCPeerConnection and data channels
Handle ephemeral token-based authentication with 60-second expiration cycles
Build resilient audio pipelines with automatic network condition handling
Configure SDP (Session Description Protocol) for WebRTC capability negotiation
Master practical implementation details:
Audio capture via mediaDevices API
Data channel event handling
NAT traversal protocols
Secure token rotation
Media stream optimization
Deep dive into production-ready code examples:
Client-side WebRTC setup
Server-side token generation
Audio pipeline configuration
Event message handling
Security boundary implementation