Inference Scaling for Long-Context Retrieval Augmented Generation
Solves RAG performance plateau by optimizing computation allocation with Inference scaling
Nice @GoogleDeepMind Paper
Solves RAG performance plateau by optimizing computation allocation with Inference scaling
📌 Achieves 58.9% performance gain over standard RAG approaches.
📌 Shows linear scaling between computation and RAG performance.
Original Problem 🔍:
RAG performance plateaus with increasing context length due to ineffective utilization of knowledge and LLMs' limited ability to process ultra-long sequences.
Solution in this Paper 🧠:
• DRAG: Incorporates extensive documents and in-context examples
• IterDRAG: Decomposes complex queries into sub-queries with interleaved retrieval
• Computation allocation model: Predicts optimal inference parameters for RAG
• Inference scaling laws: Quantifies relationship between RAG performance and computation
Key Insights from this Paper 💡:
• RAG performance scales almost linearly with increasing inference computation when optimally allocated
• DRAG excels with shorter context lengths, while IterDRAG scales better for longer contexts
• Performance gains diminish beyond 1M tokens, suggesting limitations in long-context modeling
• Optimal configurations can be predicted using the computation allocation model
Results 📊:
• Up to 58.9% performance gains on benchmark datasets compared to standard RAG
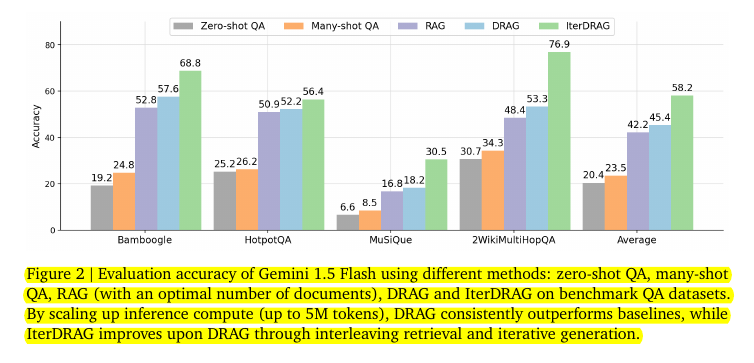
• DRAG and IterDRAG consistently outperform baselines across various tasks
• Computation allocation model achieves 96.6% of optimal performance when generalizing to unseen domains
• Accurate predictions for target lengths below 1M tokens when extrapolating to longer context lengths
This paper explores how to effectively scale up inference computation for RAG tasks using long-context large language models (LLMs). The authors introduce two main strategies:
Demonstration-based RAG (DRAG): This approach incorporates both extensive retrieved documents and in-context examples to utilize the capabilities of long-context LLMs.
Iterative demonstration-based RAG (IterDRAG): This method decomposes complex queries into simpler sub-queries and uses interleaved retrieval and generation steps to construct reasoning chains.
Evaluation accuracy of Gemini 1.5 Flash using different methods: zero-shot QA, many-shot QA, RAG (with an optimal number of documents), DRAG and IterDRAG on benchmark QA datasets