Knowledge-Aware Query Expansion with Large Language Models for Textual and Relational Retrieval
LLMs now understand both text and relationships in documents by using knowledge graphs as a bridge.
LLMs now understand both text and relationships in documents by using knowledge graphs as a bridge.
Knowledge-Aware Retrieval (KAR) framework, proposed in this paper, teaches LLMs to see connections between documents, not just words.
Original Problem 🎯:
Current query expansion methods focus mainly on textual similarities, overlooking important document relations in semi-structured search queries. This leads to suboptimal search results when users have both textual and relational requirements.
Solution in this Paper 🛠️:
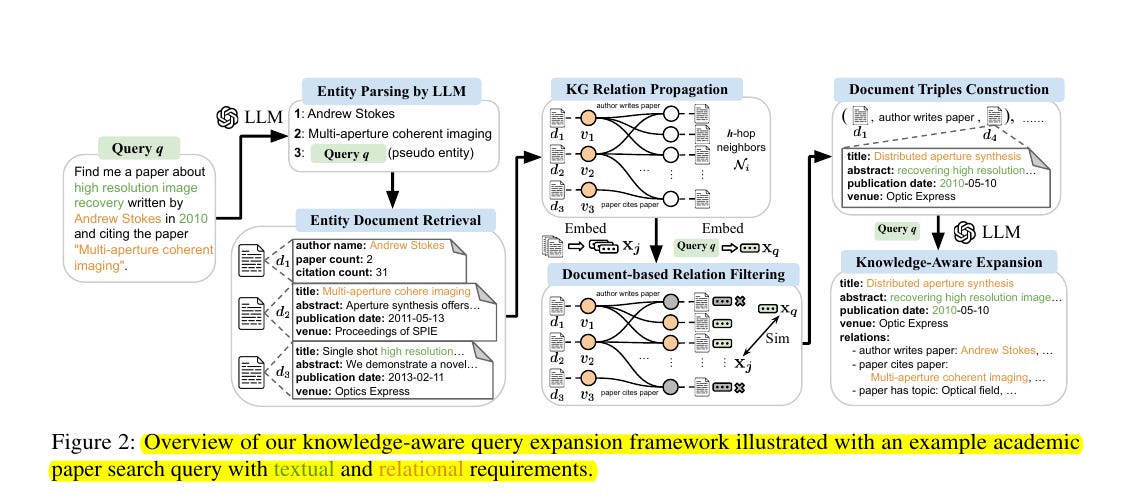
• Introduces Knowledge-Aware Retrieval (KAR) framework that augments LLMs with structured document relations from knowledge graphs
• Uses document texts as rich knowledge graph node representations
• Implements document-based relation filtering to extract query-focused relations
• Employs two-step LLM inference: first for entity parsing, then for knowledge-aware expansion
• Constructs document triples combining textual and relational information
Key Insights from this Paper 💡:
• Document texts provide richer node representations than entity names alone
• Structured document relations improve query expansion quality
• Two LLM inferences per query maintain reasonable latency
• Knowledge graphs effectively ground LLM generations to domain-specific facts
Results 📊:
• Outperforms state-of-the-art baselines on AMAZON, MAG, and PRIME datasets
• Achieves better or comparable performance to supervised methods
• Shows consistent improvement across different retrievers (BM25, dense embeddings)
• Maintains practical latency compared to other LLM-based approaches
• Demonstrates effectiveness with both GPT-4 and LLaMA-3.1-8B
💡 The knowledge-aware query expansion framework called KAR works by:
Using LLMs to parse entities from queries
Retrieving relevant document texts
Propagating through knowledge graph relations
Filtering relations using document-based scoring
Constructing document triples
Generating knowledge-aware query expansions