LightRAG: Simple and Fast Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Graph-powered RAG system LightRAG, proposed in this paper, builds knowledge graphs on-the-fly to fix RAG's context blindness
Graph-powered RAG system LightRAG, proposed in this paper, builds knowledge graphs on-the-fly to fix RAG's context blindness
Original Problem 🔍:
Current Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems struggle with flat data representations and lack contextual awareness, leading to fragmented answers that fail to capture complex interdependencies between topics.
Solution in this Paper 🛠️:
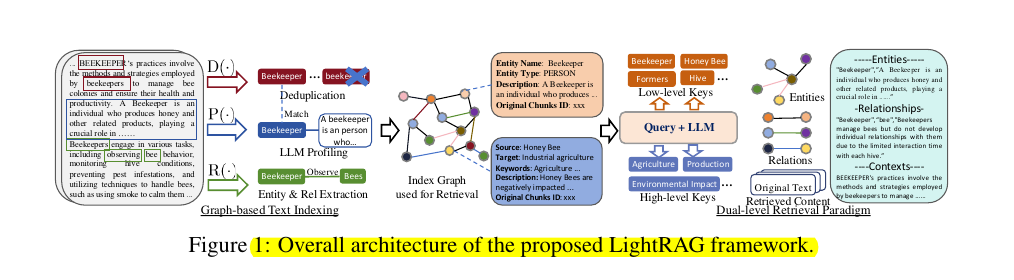
• LightRAG introduces graph-based text indexing with dual-level retrieval paradigm
• Uses LLMs to extract entities and relationships from text chunks
• Implements dual-level retrieval: low-level for specific entities and high-level for broader themes
• Features incremental update algorithm for seamless integration of new data
• Combines graph structures with vector representations for efficient entity retrieval
Key Insights from this Paper 💡:
• Graph structures excel at representing complex interdependencies between entities
• Dual-level retrieval enhances both specific and abstract information gathering
• Incremental updates eliminate need for complete index rebuilding
• Vector-based entity retrieval reduces overhead compared to community-based traversal
• Original text can be omitted without significant performance loss
Results 📊:
• Outperforms baselines across all datasets, especially in Legal domain (82.54% win rate)
• Shows superior diversity metrics (89.02% in Legal dataset)
• Demonstrates better comprehensiveness (80.95% vs baselines' ~20%)
• Achieves significant efficiency gains with reduced API calls and token usage
• Maintains performance while handling incremental updates
🛠️ LightRAG consists of:
Graph-based text indexing that extracts entities and relationships using LLMs
Dual-level retrieval paradigm combining low-level (specific entities) and high-level (broader topics) information
Integration of graph structures with vector representations for efficient retrieval
Incremental update capability for handling new data