LLMs Are Killing Your Writing Fingerprints: MIT Research
LLM dependence weakens writers, LLMs performed very bad on competitive coding, Google drops Gemini 2.5 FlashLite API; OpenAI Microsoft tensions; finance AI Agents displace pros
Read time: 7 min
📚 Browse past editions here.
( I publish this newletter daily. Noise-free, actionable, applied-AI developments only).
⚡In today’s Edition (17Jun-2025):
🧠 New MIT research finds that dependence on LLMs weakens a writer’s neural and linguistic fingerprints
😯 BAD News for LLMs: New Benchmark finds the best Frontier LLMs got 0% on Hard Competitive Coding Problems
📢 Google release Gemini 2.5 Flash Lite (API only)
🗞️ Byte-Size Briefs:
OpenAI and Microsoft Tensions Are Reaching a Boiling Point
AI agents will automate finance workflows, displace professionals
DeepSeek-r1 (MIT Licensed open-sourced model) ties Opus 4, tops WebDev Arena
🧠 New MIT research finds that dependence on LLMs weakens a writer’s neural and linguistic fingerprints
A hefty 206-page MIT paper’s findings are super concerning for the future of human creativity.
"LLM users consistently underperformed at neural, linguistic, and behavioral levels"
Relying only on EEG, text mining, and a cross-over session, the authors show that keeping some AI-free practice time protects memory circuits and encourages richer language even when a tool is later reintroduced.
🧠 What the researchers did
Fifty-four Boston students sat for three timed essay sessions. One group could ask ChatGPT for every sentence, another could search Google, and a third worked from memory alone. A 32-channel EEG cap tracked brain activity while software logged each prompt, keystroke, and revision. Some volunteers then wrote a fourth essay with a tool they had not used before, giving the researchers a before-and-after view of what happens when help is added or withdrawn.
Key Findings on 𝐁𝐞𝐡𝐚𝐯𝐢𝐨𝐫𝐚𝐥 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐂𝐨𝐠𝐧𝐢𝐭𝐢𝐯𝐞 𝐄𝐧𝐠𝐚𝐠𝐞𝐦𝐞𝐧𝐭
- Quoting Ability: LLM users failed to quote accurately, while Brain-only participants showed robust recall and quoting skills.
- Ownership: Brain-only group claimed full ownership of their work; LLM users expressed either no ownership or partial ownership.
- Critical Thinking: Brain-only participants cared more about 𝘸𝘩𝘢𝘵 and 𝘸𝘩𝘺 they wrote; LLM users focused on 𝘩𝘰𝘸.
- Cognitive Debt: Repeated LLM use led to shallow content repetition and reduced critical engagement. This suggests a buildup of "cognitive debt", deferring mental effort at the cost of long-term cognitive depth.
🧠 What the signals show
When students wrote unaided, alpha and beta waves flowed briskly between parietal and frontal regions, a pattern linked to deep semantic processing and memory rehearsal. Google softened that flow but left it functional. ChatGPT flattened it the most, hinting that an external language model can short-circuit internal rehearsal. Students who started with ChatGPT and later went tool-free kept the sluggish pattern, showing cognitive debt. By contrast, students who first wrote unaided and then tried ChatGPT lit up wide networks, suggesting that prior brain exercise keeps circuits ready even when automation enters the scene.
✍️ What the words show
Embedding space is a numerical map where every essay turns into one point based on its meaning and style.
ChatGPT essays land close together in that map, which shows they share similar wording and structure. The model pushes writers toward phrases and facts that sit at the center of its training distribution, so different people end up sounding alike. That sameness is also clear when the software counts named entities; ChatGPT drafts recycle the same examples instead of pulling from personal memory.
Google-assisted essays sit between the extremes. Search results add some outside phrasing, but writers still choose what to copy, so their texts overlap less than ChatGPT’s yet more than fully original work.
Brain-only essays scatter across the map. Each writer relies on lived experience and unique vocabulary, so the statistical distance between any two essays grows. Diversity here signals deeper internal retrieval and richer personal voice.
The crossover test shows habit matters. Students who first wrote unaided kept that diversity even after adding ChatGPT, because their earlier sessions trained them to steer the tool and inject their own ideas. Students who started with ChatGPT struggled to regain variety when the tool was taken away; their early reliance narrowed the mental paths they later needed for solo writing.
In short, text mining reveals that large language models compress individual style, while prior tool-free practice protects it and even helps users bend the model to their will when they choose to. READ THE FULL RESEARCH HERE.
Recall scores : Percentage of participants within each group who struggled to quote anything from their essays in Session
Recall scores complete the picture. Remembering one’s own sentences proves that the words passed through working memory instead of being pasted from an external source. High recall in the brain-only group and low recall in the ChatGPT group confirm that heavier automation weakens both ownership and memory trace.
After writing, only 17 % of ChatGPT users could quote their own sentences, versus 89 % in the brain-only group.
ChatGPT writers also reported the weakest sense of authorship, matching EEG evidence of reduced self-monitoring hubs.
📈 Takeaways
Large language models ease surface workload but also mute the neural and linguistic fingerprints that mark genuine learning. Regular tool-free practice keeps memory circuits active and sustains individual voice, making later automation a boost rather than a crutch. For anyone who writes with AI, the best insurance is to draft at least some pieces with nothing but the mind’s own search engine.
😯 BAD News for LLMs: New Benchmark finds the best Frontier LLMs got 0% on Hard Competitive Coding Problems
What is LiveCodeBench Pro?
LiveCodeBench Pro is a new daily-updated competitive programming benchmark that’s composed of problems from Codeforces, ICPC, and IOI (“International Olympiad in Informatics”). It’s continuously updated to reduce the likelihood of data contamination.
And Codeforce ICPC is a team-based, multi-stage global university championship lasting several hours with emphasis on collaboration and performance under pressure. Teams of three undergraduate students tackle 8–15 algorithmic problems over 5 hours. After regional qualifiers, top teams advance to the ICPC World Finals.
🗂️ Building the Benchmark
A medal-winner team harvests each Codeforces, ICPC, and IOI problem as soon as a contest ends, before editorials appear, wiping out training leakage.
They store 584 tasks and tag each one as knowledge, logic, or observation heavy, producing a balanced skill matrix .
What the paper finds?
Though some report that LLMs now surpass elite programmers, the LiveCodeBench Pro benchmark—curated and reviewed by Olympiad medalists—demonstrates they still fall short. The leading model solves only about 53% of medium‐difficulty problems (and none at the hardest level), excels mainly at routine implementations, and frequently fails at deep algorithmic reasoning or complex case analysis. These results suggest current advances rely more on coding precision and tool support than genuine problem-solving, leaving a substantial gap to human grandmasters.
The figure shows the “LiveCodeBench Pro” leaderboard, plotting each model’s Codeforces‐style Elo rating (a measure of problem-solving skill) against its average dollar-cost per problem.
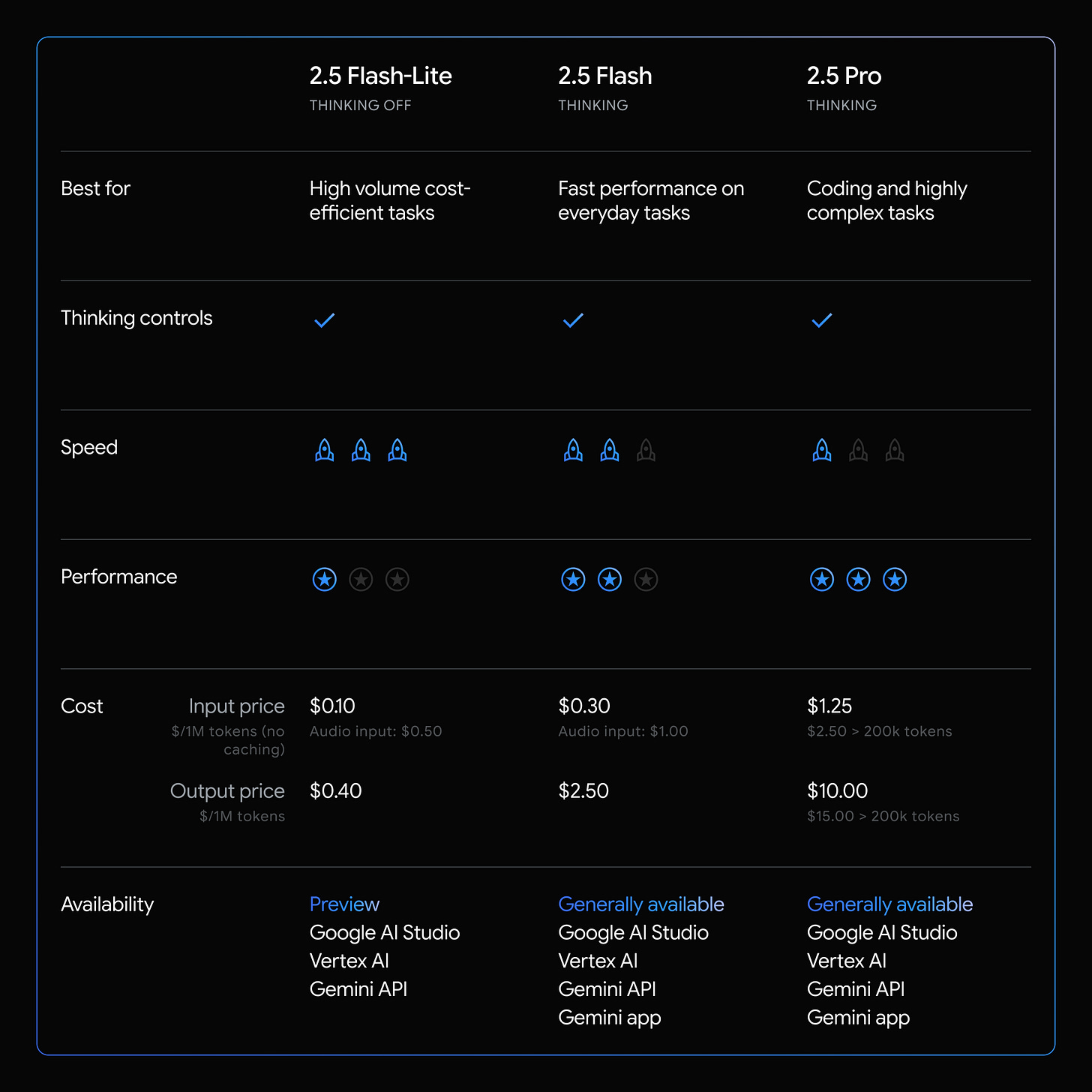
📢 Google release Gemini 2.5 Flash Lite (API only)
⚡️ Google launches Gemini 2.5 Flash and also the stable versions of Gemini 2.5 Flash and Pro.
These hybrid reasoning models sit at the cost-speed Pareto frontier. They power apps like Spline, Rooms, and services at Snap and SmartBear.
The preview of Gemini 2.5 Flash-Lite debuts as the fastest, most cost-efficient 2.5 model. It outperforms 2.0 Flash-Lite on coding, math, science, reasoning, and multimodal benchmarks.
Flash-Lite handles translation and classification with lower latency than 2.0 Flash and 2.0 Flash-Lite. It retains Gemini 2.5 features like tool connections, code execution, multimodal input, and a one-million-token context window.
Flash, Pro, and Flash-Lite preview are now in Google AI Studio, Vertex AI, and the Gemini app. Custom versions of Flash and Flash-Lite also integrate with Search, and feedback is welcome.
And in terms of Price per token Google is in a leading position.
🗞️ Byte-Size Briefs
OpenAI considers antitrust complaint to challenge Microsoft’s cloud dominance and secure fairer contract terms for AI hosting. As per news retports, OpenAI may, challenge Microsoft’s Azure exclusivity, and address concerns over investor leverage (from Microsoft) obstructing nonprofit-to-public benefit conversion, while OpenAI secures alternative cloud partnerships and navigates legal, regulatory and corporate pressures to diversify AI infrastructure.
Robert F. Smith warns autonomous AI agents will automate repetitive finance workflows, displacing most professionals within a year. Smith highlights that AI replication of document handling and spreadsheet tasks cuts costs and scales operations at near-zero expense, enabling 40% augmented employees and prompting 60% professionals to seek new roles after his SuperReturn Berlin address to 550 private-equity investors.
New DeepSeek-r1 (0528) ties Claude Opus 4 for WebDev Arena #1 in lmarena.ai. Shows that an MIT-licensed open LLM can match closed-source performance. It also ranks sixth overall in Text Arena, secures second in Coding tasks, fourth in Hard Prompts and fifth in Math, highlights version 0528 performance, and its MIT license makes it the current top open-source LLM on the global leaderboard.
That’s a wrap for today, see you all tomorrow.