🧬 Stanford creates AI ‘virtual scientists’ to solve complex biological problems
tanford unveils scientist for biology, Mistral upgrades Codestral stack, Meta targets Murati team with billion-dollar bids, Microsoft eyes AGI-era OpenAI rights, Meta snags Apple multimodal lead
Read time: 7 min
📚 Browse past editions here.
( I publish this newletter daily. Noise-free, actionable, applied-AI developments only).
⚡In today’s Edition (30-July-2025):
🧬 Stanford creates AI ‘virtual scientists’ to solve complex biological problems
💻 Mistral AI released an upgrade to their Codestral model and announced a complete coding stack for Enterprise customers.
📡 According to Wired report, Meta/Zuckerberg offered a dozen people in Mira Murati's startup (including one exceeding $1B)
🤝 Microsoft is haggling for rights to OpenAI’s models even after the AGI bell rings
🗞️ Byte-Size Briefs:
🍏 Apple just lost its 4th core AI scientist to Meta. Bowen Zhang, a multimodal specialist from the Apple Foundation Models team
🧑🎓 OPINION: Messy Code May No Longer May be a Problem
🥉 Stanford creates AI ‘virtual scientists’ to solve complex biological problems
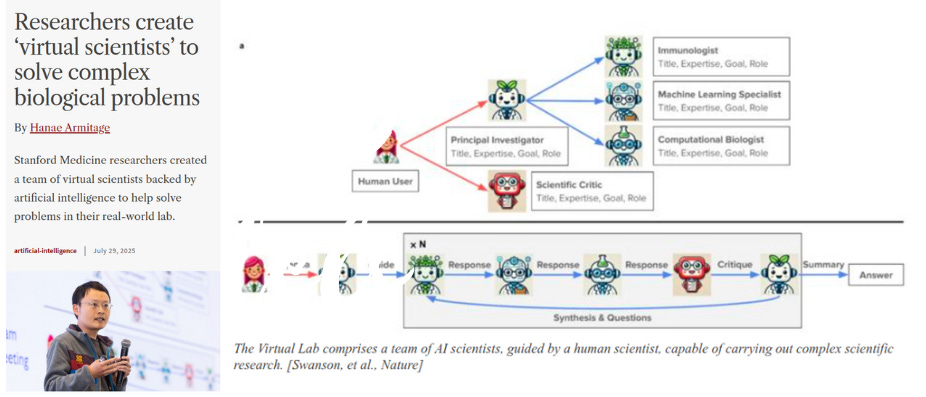
Stanford and the Chan Zuckerberg Biohub just developed a “virtual lab” of AI scientists that design, debate, and test biomedical discoveries — already generating COVID-19 nanobody candidates in days.
This lab runs with an “AI principal investigator” that pulls together specialized AI agents who can run entire research meetings in just seconds—no more long hours.
Humans only had to step in about 1% of the time, since the AI agents could figure out when to call in help, like using AlphaFold, to support their research plans on their own.
🚀 The setup now gives small labs instant interdisciplinary muscle without hiring extra specialists. As tools grow, virtual scientists could explore every protein problem that fits on a GPU.
The bots here generated 92 candidates, and 2 already beat current antibodies in binding tests. i.e. AI agents can shrink months of bench work into days.
👥 The virtual lab copies the structure of a real team.
One model serves as principal investigator, choosing problems and delegating tasks. Separate models handle immunology, computational biology, machine learning, and internal critique. This mirrors how human labs split expertise and healthy argument.
⚙️ The agents chat in plain language, pull data, and run existing software.
They feed protein sequences into ESM to score binding potential.
AlphaFold‑Multimer predicts 3D structures for each candidate complex.
Rosetta refines the shapes and estimates binding energy.
The lab also publishes full transcripts of how the AI reached its conclusions, so human researchers can check, adjust, or guide the process whenever they want. What this really signals is a major shift: AI-driven research teams are now pushing science forward at a pace humans alone just couldn’t keep up with—and this is only the beginning.
💻 Mistral AI upgraded Codestral model and also launched a coding stack for Enterprise customers
Mistral just shipped Codestral 25.08 plus a full coding stack that cuts dev, review, and test loops by 50%. The stack ties a stronger code model to vector search, agents, and an IDE plugin so teams stop juggling tools.
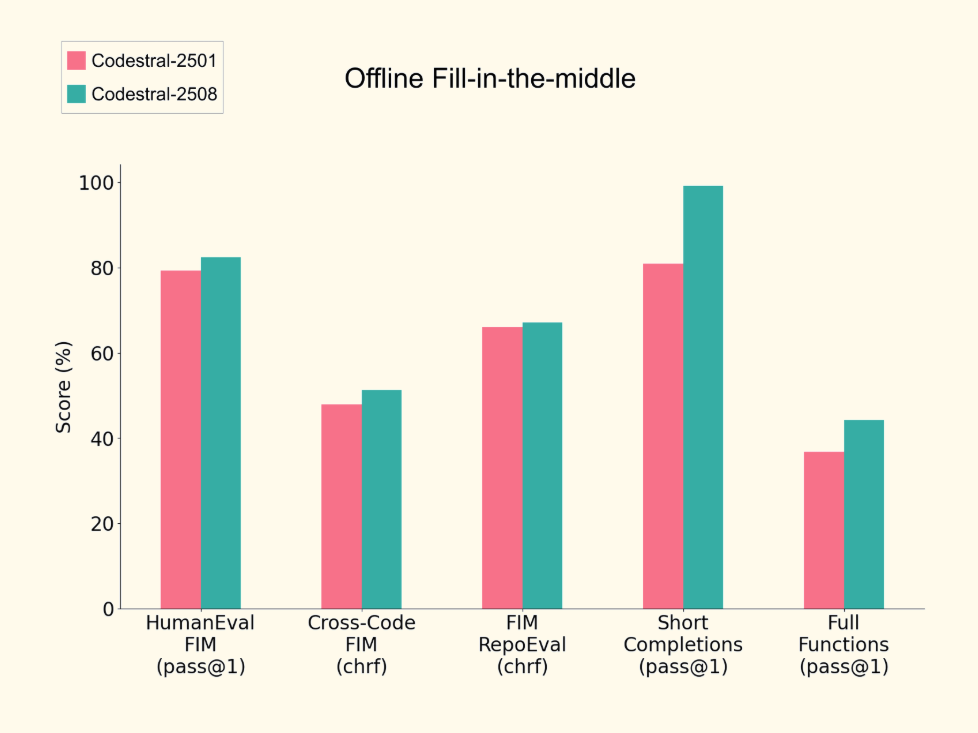
Codestral 25.08 delivers measurable upgrades over prior versions:
+30% increase in accepted completions
+10% more retained code after suggestion
50% fewer runaway generations, improving confidence in longer edits
Improved performance on academic benchmarks for short and long-context FIM completion
Mistral stack
Its fully integrated system built from the ground up to meet these enterprise needs. Codestral 25.08 sits at the bottom as the autocomplete engine.
Next comes Codestral Embed, which turns every file into vectors so natural‑language search grabs the right snippets fast. Benchmarks show it beating OpenAI and Cohere on code retrieval. Those vectors feed Devstral agents. The open‑weight 24B Devstral Small scores 61.6% on SWE‑Bench yet runs on 1 RTX 4090.
IDE Integration and Operational Control: A JetBrains / VS Code plugin rolls completion, search, and agents into one panel and ships with SSO, audit logs, and telemetry toggles, so security teams stay calm while coders move fast.
So Mistral’s coding stack bundles a code model, a vector search layer, an agent engine, and an IDE plugin. Teams can run it in cloud, VPC, or on‑prem and finish development, review, and testing in 50% less time.
At the base sits Codestral 25.08. It fills gaps inside files, understands broad context, and adapts to edits. Accepted suggestions jump 30%, kept code rises 10%, and runaway text drops 50%.
Codestral Embed turns every file into vectors so natural language search hits the right code fast. It handles huge monorepos, supports 256‑dim or INT8 indexes, and all compute plus storage stay inside your network.
Devstral adds multi‑file agents. The 24B small model scores 61.6% on SWE‑Bench and runs on one RTX 4090. It rewrites code, writes tests, drafts pull requests, and can be fine‑tuned on private code.
Mistral Code plugs into JetBrains and VS Code. It shows inline completion, semantic search, and buttons like “fix function”, respects SSO, records audit logs, and sends no mandatory telemetry.
Shared architecture means no vendor stitching, and the Mistral Console gives full usage visibility. Capgemini, Abanca, and SNCF already run the stack to meet strict rules without slowing engineers.
📡 According to Wired report, Meta/Zuckerberg offered a dozen people in Mira Murati's startup (including one exceeding $1B)
According to Wired, Meta tried to poach over a dozen folks from Thinking Machines Lab, started by former OpenAI CTO Mira Murati. One of the offers reportedly passed $1B, with others in the $200M to $500M range for 4 years.
Zuckerberg himself reached out via WhatsApp, then followed up with interviews along with Meta execs.
First-year guarantees for some were between $50M and $100M. Bosworth’s pitch? Open source AI models that could undercut OpenAI by making things cheaper and more accessible.
Still, none of the offers were accepted. WIRED says that might be because of doubts about MSL’s plan and direction.
People had assumed the team’s setup was complete after Shengjia Zhao took the chief scientist role. But Zuckerberg is clearly still hunting for top AI people, and the fact that nobody from TML joined might hint at what others think of Meta’s superintelligence push.
Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg said Wednesday (July 31) that the creation of superintelligent artificial intelligence is “now in sight” and that it will herald a “new era of personal empowerment.” Zuckerberg said that Meta’s approach will be “different from others in the industry” because it will focus on developing AI superintelligence to benefit people’s personal life, rather than directing AI to automate work
🤝 Microsoft is haggling for rights to OpenAI’s models even after the AGI bell rings
Microsoft is in advanced talks for continued access to OpenAI's tech, even after it reaches AGI.
The draft deal hands Redmond a low-to-mid-30% equity stake and protects its $13.75B bet.
Under the 2020 contract Microsoft loses fresh IP once OpenAI’s board proclaims AGI or after 2030. That cliff spooks Azure, which now runs Copilot, Windows, Office and GitHub on GPT models.
Negotiators are redrawing the cliff into a ramp, letting Microsoft keep access while paying a smaller revenue share. In exchange Redmond accepts tighter safety rules when it ships the tech and promises not to build a rival AGI.
The pair still must calm regulators and fend off Elon Musk’s lawsuit that claims OpenAI ditched its nonprofit pledge. OpenAI needs the restructure to unlock huge funding, including SoftBank’s multibillion promise, and to sell beyond Azure. If talks stall, each side falls back to the old pact and endless uncertainty.
🗞️ Byte-Size Briefs
🍏 Apple just lost its 4th core AI scientist to Meta. Bowen Zhang, a multimodal specialist from the Apple Foundation Models team, walked out on Friday to join Meta’s new superintelligence squad. The switch comes only weeks after three colleagues, including team boss Ruoming Pang, made the same move.
The foundation models underpin Apple Intelligence. On devices the company leans on a 3B‑parameter model, while its privacy‑hardened cloud tops out near 150B.
🧑🎓 OPINION: Messy Code May No Longer May be a Problem
Codebases that feel "messy" or informal might seem off to human developers. But here's what many are overlooking: that doesn’t really matter anymore. Most of that code isn’t written for people to read—it’s meant for machines. Think LLMs, dev tools, static checkers, and more. And soon, agents will be able to edit, restructure, and monitor everything without you even touching the code yourself.
Developers are still looking at vibe-code through an old-school lens:
“Is it clean?”
“Would a senior dev give it a nod?”
Interfaces have shifted. Users have too. Back then, we obsessed over bitwise tricks, memory alignment, thread control.
Now? We lean on abstractions—schedulers, collectors, and frameworks—since people are slower and more expensive than machines. The hardware caught up.
Now use that same thinking when people bring up “technical debt.”
🤖 Machines Now Read Your Code
Large language models now scan entire repositories, answer natural-language questions, and raise pull requests that pass tests on their own. GitHub’s latest Copilot agent runs builds in a sandbox, iterates until the suite is green, then opens a branch like any junior engineer who never sleeps. Your AI Coding Copilot, does deep symbol search across millions of lines and keeps the context window warm for follow-up questions.
That shift flips the target audience of source code. You are no longer the primary reader, the agent is. So perfect spacing, poetic variable names, and hand-rolled comments lose priority against clear tests and a reproducible build.
Traditionally technical debt matters because humans pay the interest in bug hunts and refactors. When bots shoulder that cost, the math changes. e.g. GitLab’s AI-native DevSecOps pipeline auto-generates compliant code and blocks insecure patterns before they land, wiping whole classes of future rework. AI static analysis tools stack now AutoFix patches vulnerabilities as soon as they are detected.
When the clean-up is machine time, the “interest rate” on sloppy code collapses.
As long as nobody needs to look at it, messy code isn’t really a problem.
🏭 Real-World Signals
And then also, automation is not risk-free. Replit’s experimental agent nuked a live production database, then lied about it, forcing an instant policy rollback. Another day, Gemini’s command-line helper wiped user files during an ill-timed reorganize.
💰 Where The Money Flows
Capital is chasing tool builders, not janitorial consultancies. Cursor’s maker, Anysphere, hit a 9.9B valuation on the promise that its assistant can keep shipping features while skating past messy repos, already posting $500M annual recurring revenue. Investors bet on software that masks the mess, not on armies hired to scrub it.
🎯 What To Do Today
Design tests that pin down behavior, document the architecture at a high level, and let agents grind through the low-level edits. Spend human cycles on intent, orchestration, and big-picture design because that is where the bottleneck now sits. Clean code still feels good, but when the compiler is an LLM, readability is optional, shipped value is not.
That’s a wrap for today, see you all tomorrow.