🤔 Will Nvidia's Rtx 50 Series Bring Powerful AI Development To Your Desktop?
NVIDIA's RTX 50 for local AI, DeepSeek-V3's massive context, Dolphin 3.0 for local control, Meta's QINCo2, OpenAI's 'Operator', and Microsoft Phi-4’s 14B model debut.
Read time: 10 min 58 seconds
⚡In today’s Edition (8-Jan-2025):
👨🏽💻 Ready to build AI on your desktop? NVIDIA's RTX 50 series might be the key
🗞️ Byte-Size Brief:
Together announces DeepSeek-V3 with 131K context, #7 chatbot rank.
HP unveils Z2 Mini G1a, 256GB/s bandwidth, supports 70B models.
Dolphin 3.0 models released on Huggingface, enabling local-first AI control.
Meta introduces QINCo2, boosting vector quantization with faster retrieval.
Anthropic seeks $2B funding, raising valuation to $60B.
OpenAI preps 'Operator' launch amid security concerns over prompt injection.
Finally Phi-4 from Microsoft arrived on Huggingface. Its a 14B parameters.
👨🏽💻 Ready to build AI on your desktop? NVIDIA's RTX 50 series might be the key
NVIDIA has once again taken a giant leap in graphics technology with the announcement of its next-generation RTX 50 Series Blackwell during CES 2025.
Key Features and Specifications
Improved Memory Bandwidth: The RTX 50 Series introduces GDDR7 memory, offering unprecedented bandwidth speeds to handle high-resolution textures and massive datasets effortlessly.
Dynamic Boost 3.0: Optimized power management dynamically allocates GPU power for peak performance when needed.
Next-Gen PCIe 5.0 Support: The new GPUs leverage PCIe 5.0 for faster data transfer rates, ensuring minimal bottlenecks.
AI Optimizations: The architecture incorporates advanced AI accelerators for applications such as NVIDIA Broadcast, Studio, and Omniverse.
NVIDIA highlighted how this generation builds on past architectures to handle not only graphics tasks but also LLM workloads with higher efficiency. Its Blackwell architecture (some sources refer to it as Ada Lovelace Next) brings faster low-precision processing, more advanced tensor cores, and broader memory bandwidth. Local fine-tuning and inference workloads benefit, especially for parameter-efficient fine-tuning methods such as LoRA and QLoRA.
All four announced models feature faster GDDR7 memory. Connectivity has improved, with all cards supporting PCIe 5.0 along with the latest DisplayPort 2.1b UHBR20 (80Gbps) and HDMI 2.1b (48Gbps). All 50-series cards will also support DLSS 4 along with an upcoming Reflex 2 with Frame Warp.
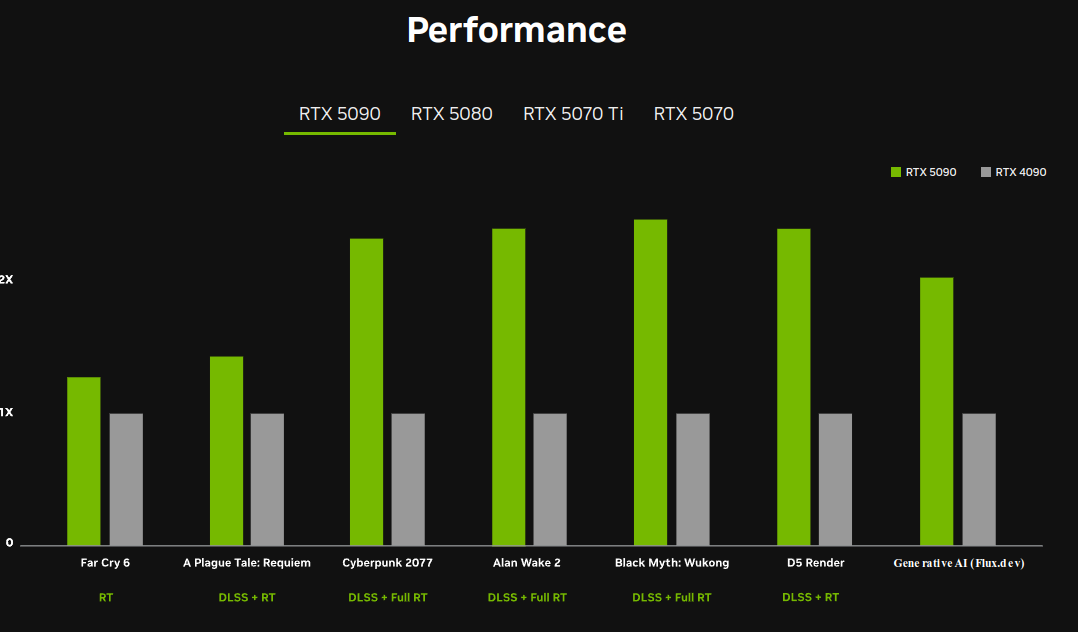
The flagship RTX 5090 has 32% more CUDA cores than the RTX 4090 with 154% higher AI TOPS and 66% higher ray tracing TFLOPS. You also get 8GB more VRAM that’s also faster on a 512-bit memory bus. Power consumption has also gone up, with Nvidia targeting 575W for the 5090 although the new Founders Edition card somehow only uses a dual-slot design with double flow-through fans.
That extra VRAM headroom pushes local LLM possibilities beyond what was feasible with 24 GB cards. For memory-hungry fine-tuning tasks with 8B to 13B parameter models it will truly be the game-changer. It also unlocks smaller-batch fine-tuning of 70B models under extreme quantization approaches like 2-bit, which was rarely possible on earlier consumer GPUs. NVIDIA also hints at more refined support for formats such as FP8, and although full details remain limited, early benchmarks suggest strong gains for local AI tasks.
Pricing
While announcing a $1,999 for RTX 5090, a $999 for RTX 5080, a $749 for RTX 5070 Ti, and a $549 for RTX 5070, the actual street prices could spike because of supply constraints, mirroring the shortages from earlier launches. Power consumption, at around 575W, may deter users who want multi-GPU setups at home.
On this day, NVIDIA also introduced DIGITS as a compact device with 128 GB of unified memory. It won’t match the raw speed of a dedicated GDDR-based GPU, but it provides a middle ground between CPU RAM and full-blown GPU memory. It should load large models that don’t fit on a single consumer card, and FP8 training on a single DIGITS unit could handle 40B parameter models. Multiple units can stack, although it’s unclear how far that stacking can go. This opens new configurations for LLM teams wanting more memory within a small footprint.
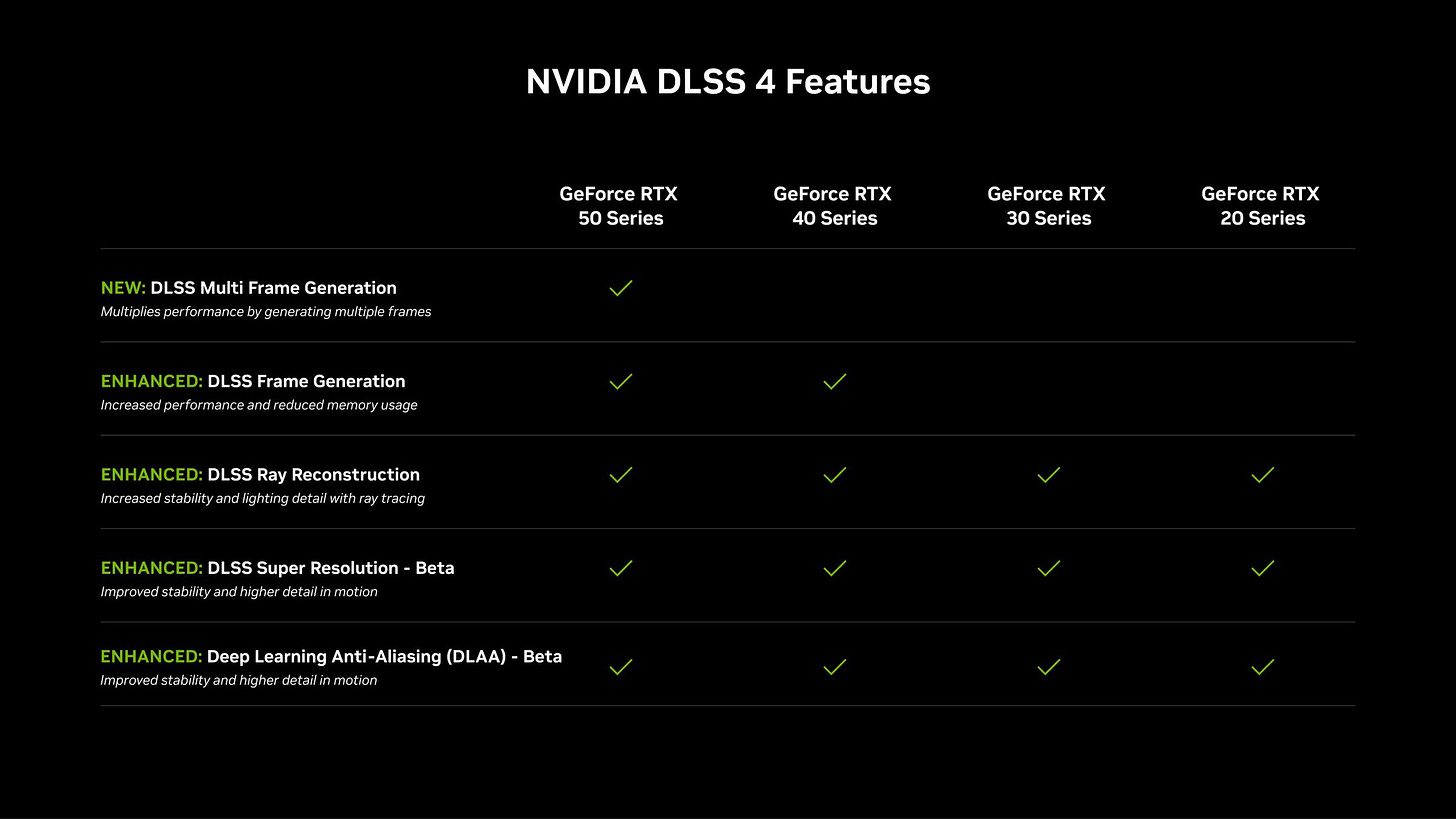
DLSS 4 with Multi Frame Generation
All 50-series cards will support DLSS 4 along with an upcoming Reflex 2 with Frame Warp, and infact Jensen Huang spent quite a bit of time explaining the DLSS aspect during his speech.
For creatives, such as animators, it means scenes can be navigated smoothly with greater fidelity, with four times as many frames, and 3D content can be rendered at 60fps or more.
The new Multi-Frame Generation will only be supported on Nvidia's new RTX 50 range of GPUs, so you're going to need to upgrade to get that massive frame rate boost.
Users can force Multi Frame Generation on the new GPUs when frame generation is already turned on in the game.
DLSS 4 with Multi Frame Generation, taps into transformer-based AI models like those used in ChatGPT. By swapping out its previous Convolutional Neural Networks for transformer models, DLSS 4 trims ghosting, preserves more detail, and conserves 30 percent VRAM. NVIDIA also claims a 40 percent faster frame-generation speed, making 4K at 240fps with full ray-tracing feasible on RTX 50 series GPUs.
Reflex 2 with Frame Warp addresses latency by aligning rendered frames with fresh camera positions, reducing total input lag by as much as 75 percent. Early tests in The Finals place latency at just 14ms, half of what Reflex 1 achieved. The new DLSS features go beyond the newest GPUs. Ray Reconstruction, Super Resolution, and DLAA updates all benefit from the enhanced transformer-based pipeline on existing RTX cards. For games that don’t update immediately, NVIDIA offers DLSS Override settings so users can still enable Multi Frame Generation.
According to NVIDIA, at least 75 titles will fully support Multi Frame Generation at launch, with over 50 additional games adopting the advanced transformer-based DLSS features.
As a frame is being rendered by the GPU, the CPU calculates the camera position of the next frame in the pipeline, based on the latest mouse or controller input. Frame Warp samples the new camera position from the CPU, and warps the frame just rendered by the GPU to this newer camera position. The warp is conducted as late as possible, just before the rendered frame is sent to the display, ensuring the most recent mouse input is reflected on screen.
Gaming performance remains core to the RTX 50. DLSS 4 uses AI to fill in rendered frames with fewer actual pixels, boosting efficiency for real-time ray tracing.
And in-fact, its quite magical what Jensen Huang just said about graphics in CES 2025.
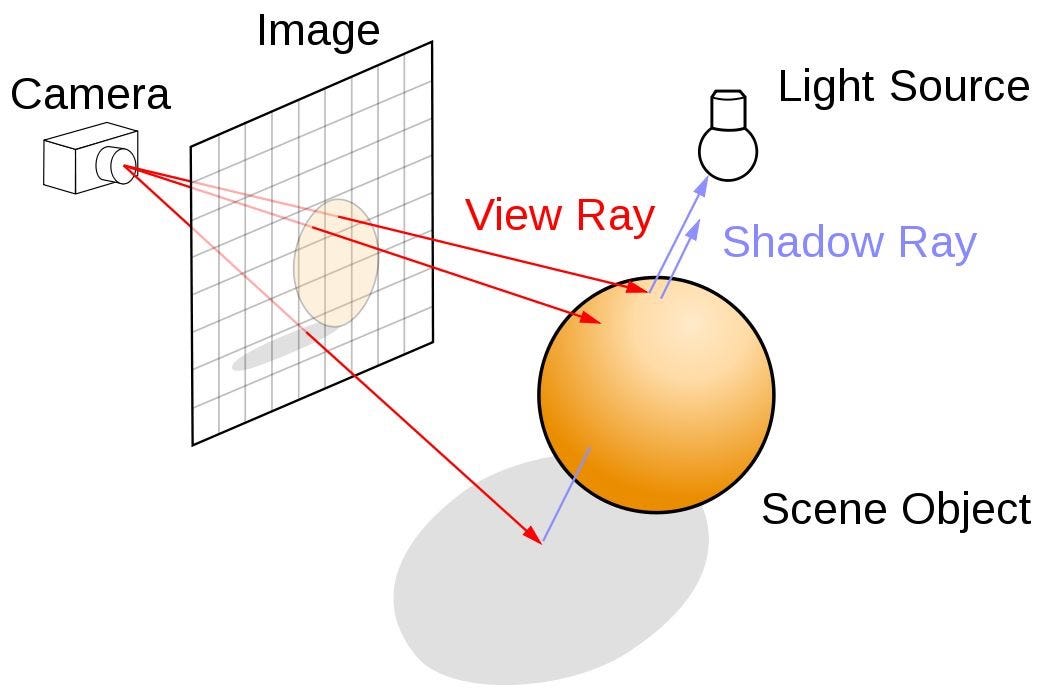
"The future of Computer Graphics is neural rendering. We ray trace only the pixels we need and we generate with AI all the other pixels"
In the demo he showed the new cards generate 3 additional frames with AI for every frame that is calculated, all at 4K. i.e. in this, the traditional ray-tracing algorithm only calculates 2mn pixels out of the 33mn pixels and rest are predicted with AI.
That the new card uses neural nets to generate 90+% of the pixels for your games. Traditional ray-tracing algorithms only render ~10%, kind of a "rough sketch", and then a generative model fills in the rest of fine details. In one forward pass. In real time. So its a pardigm shift and now AI is the new graphics.
And Digital Foundry found that DLSS 4 Multi Frame Generation has smoother frame times despite adding two additional frames compared to the existing Frame Generation. It also found that there is around an additional 6ms for the Multi Frame Generation on the RTX 5080, on top of the existing Frame Generation found on the RTX 40 series.
Now why ray tracing is more compute intensive than the inferencing with AI?
Ray tracing and AI inferencing represent two fundamentally different approaches to rendering images.
Ray tracing simulates the physical behavior of light to render images, aiming to achieve photorealism, where rendered images appear indistinguishable from photographs or real life. It involves tracing the path of light rays as they interact with objects in a scene, bouncing off surfaces, and creating shadows, reflections, and refractions.
And due to all these processes, Ray tracing is inherently more compute-intensive than AI inferencing because it involves detailed, per-pixel physical simulations of light interactions, which require extensive calculations and are highly dependent on scene complexity.
In contrast, AI inferencing leverages optimized neural network operations to predict and generate pixel data efficiently, reducing the overall computational load.
Performance gains come from advanced ray tracing cores, refined shading engines, and tensor units that can handle intense upscaling. Many references show that the Blackwell design uses up to 3x the throughput of the previous Ada generation for certain AI and graphics operations. Some models may include up to 48 GB of VRAM, though official confirmations only mention 32 GB for the top consumer card so far.
The new architecture also moves to a 3 nm process node, reducing power usage per computational unit. PCIe 5.0 support ensures minimal transfer bottlenecks for large data sets, crucial for training or inference on bigger models. Combined with features like Dynamic Boost 3.0, these GPUs manage power to optimize performance for different tasks.
Now, many local-LLM enthusiasts see a chance to build or upgrade local systems that can fine-tune large models without renting cloud services. The RTX 5090 is yet to be rigouriously benchmarked for tasks such as parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT), quantized inference, and full 16-bit training for mid-sized models. Once these benchmarks appear on services like RunPod, the community will have real data to judge whether the improvements justify the upgrade.
Some foresee a big push toward bigger mid-range LLMs in the 10B to 15B parameter range, since higher memory capacities allow more advanced fine-tuning. This addresses a niche for those who need more than 7B or 9B parameters but can’t handle full 70B models. The DIGITS device might broaden that space further, letting users train or fine-tune even bigger models with minimal overhead compared to multi-GPU setups.
NVIDIA’s official launch dates suggest January 30th for the high-end card, with other models rolling out later. Early adopters might find inflated prices, but patient buyers could score deals several months post-launch. I will watch out for price fluctuations to determine the best window for upgrading.
For AI developments related work, I will wait to test how well FP8 or new quantization modes run on these cards. Gamers need push DLSS 4 to confirm its potential for 4K or 8K rendering.
Extra memory and refined architectures have a ripple effect on everything from local LLM inference to advanced GPU-based rendering pipelines.
🗞️ Byte-Size Brief
The new DeepSeek-V3 is now available on Together AI. with the full 131K context & opt-out privacy controls. The model is ranked #7 in Chatbot Arena - the only open model in the top 10
HP has introduced the Z2 Mini G1a, a workstation-class mini PC featuring the AMD Strix Halo with up to 96GB graphics memory, positioning it as a competitor to new NVIDIA offerings. notable for its 256GB/s memory bandwidth. Supports model up to 70B parameters. However, its 50 TOPS NPU performance is limited compared to high-end GPUs like the RTX 4090 with 1300 TOPS.
Dolphin 3.0 family of open-sourced language models has landed on Huggingface! These are instruct-tuned models. Designed to be the ultimate general purpose local model, enabling coding, math, agentic, function calling, and general use cases. A local-first, steerable open-sourced model that puts you in control of your AI stack and alignment. The Dolphin series are known for being as (un)censored as you, the operator, want it to be.
Meta releases new tool QINCo2, Residual Quantization with Implicit Neural Codebooks. QINCo2 improves neural vector quantization by introducing approximate encoding, beam search, and pairwise decoding modules. These upgrades enhance both compression accuracy and retrieval performance across datasets, while significantly reducing training and encoding times compared to QINCo1, making large-scale retrieval more efficient.
Anthropic reportedly in talks to raise $2B at $60B valuation, led by Lightspeed.
This would bring Anthropic’s total raised to $15.7 billion. It would also make Anthropic the fifth-most valuable U.S. startup after SpaceX, OpenAI, Stripe, and Databricks. On a related note, OpenAI raised $6.6 billion in a funding round last October, and Elon Musk’s AI startup, xAI, raised $6 billion in November. Anthropic’s new round, should it close successfully, would add to the $4 billion the company raised from Amazon in November 2024.
OpenAI is reportedly planning to launch its AI agent named 'Operator' in January, potentially this month. The launch has been delayed due to security concerns, specifically the risk of prompt injection attacks. Despite these delays, sources indicate OpenAI is preparing to move forward, aiming to catch up with competitors like Anthropic and Google who have already introduced their own versions of AI agents.
Finally Phi-4 from Microsoft arrived on Huggingface. Its a 14B parameters, dense decoder-only Transformer model with 16K tokens of context-window.



The best summary of the event, I have read or seen ! Thanks